Urticaria (Hives)
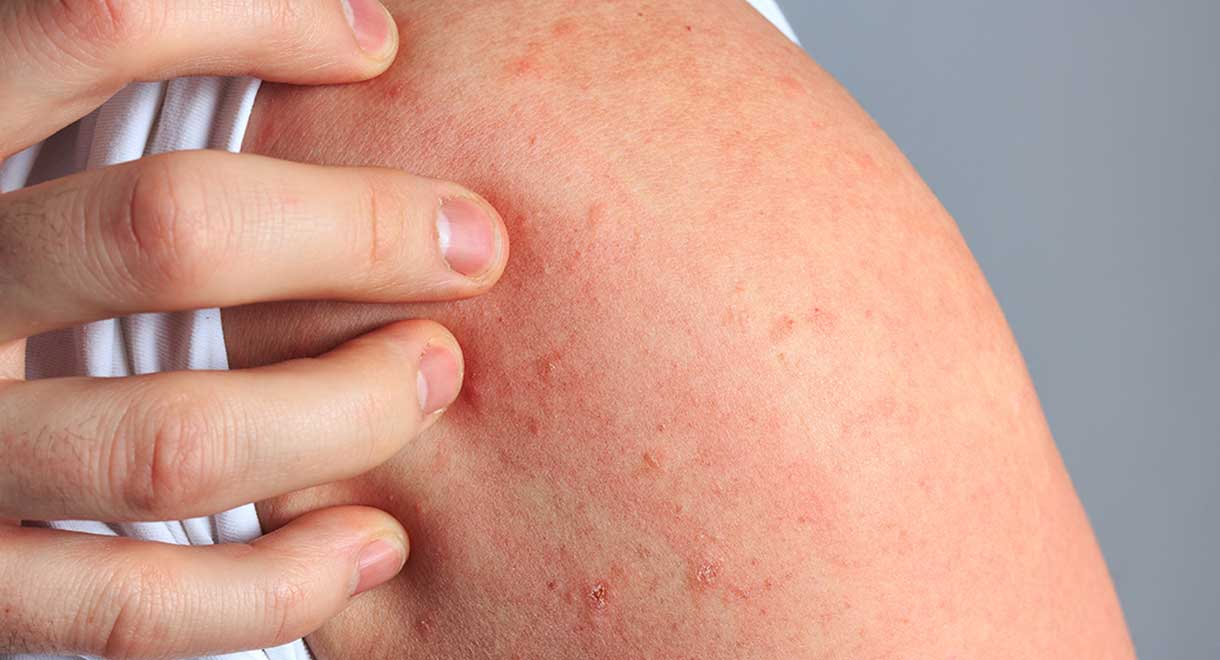
Urticaria presents as pink to reddish lumps on the skin that are very itchy. The lumps may be small to very large and may be painful, and are sometimes called hives. It can occur as a result of an allergic reaction to foods, bites or drugs, or could be an immune system reaction to components of the skin. In the latter case it is an autoimmune disease.
It’s not uncommon to experience a one off bout of hives, as a result of coming into contact with a substance you are allergic to – such as nickel, a plant or an insect sting. Some people suffer with chronic urticaria, where the condition can last for months or years.
What causes urticaria?
The following factors can all contribute:
- Food allergy or intolerance. People with urticaria usually suffer with one or more food sensitivities. Common culprits are dairy products, gluten, eggs, nuts, soy, corn, fish, shellfish, salicylates or amines. People with food sensitivities are more likely to develop allergies to chemicals, metals, medication, animals, pollen, grass, soap and other external factors, which can trigger hives.
- Stress can trigger a flare up.
- Leaky gut syndrome is an initiator and driver of urticaria, therefore it must be addressed.
- Nutrient deficiencies, particularly vitamin D and selenium.
- Genetic tendencies as chronic hives can be autoimmune in origin.
Recommendations
- An elimination diet should be followed, excluding the most common allergens, which are gluten and dairy products. Depending on the individual, other food sensitivities may also be present. A low salicylate and low amine diet may prevent them. An elimination diet is best conducted under the supervision of a healthcare practitioner.
- Follow the healthy eating guidelines in the book “Healing Autoimmune Disease”.
- Avoid industrial seed oil (“vegetable oil”) such as soy, canola, cottonseed, sunflower, safflower, grapeseed and corn oil, as it is high in omega 6 fat, which is rapidly oxidized and promotes inflammation in the body.
- Include plenty of healthy fats in the diet, such as coconut oil, avocados, ghee, olive, macadamia and avocado oil.
- If the condition worsens see an immunologist or hematologist to check for underlying blood disorders
Recommended supplements for urticaria
- Fish Oil
Take 1 capsule twice daily just before meals. The omega 3 fats in fish oil reduce inflammation and have a moisturizing effect on the skin. - Vitamin D
Take 2,000 to 5,000 I.U. daily especially during winter or if you avoid the sun; take vitamin D with food. Vitamin D insufficiency increases the risk of allergies and autoimmune conditions. Vitamin D has natural anti-inflammatory effects. - Selenomune
Take one capsule daily. Selenomune is the leading selenium supplement and is designed to support a healthy immune system. Selenomune reduces inflammation and can reduce auto-antibody production in autoimmune conditions. - Ultimate Gut Health Powder
Take 1 level scoop daily. Ultimate Gut Health keeps your intestines as healthy as possible. Designed to soothe, heal and repair the gut lining, you will find your intestines love this powder. - N-Acetyl-Cysteine (NAC)
Take 2 capsules twice daily to improve liver function and boost glutathione production.
The above statements have not been evaluated by the FDA and are not intended to diagnose, treat or cure any disease.

My son has cold utecaria and has had condition for 5 years since 17 years old . Finds condition hard when wants to go for swims in cold water but can’t . Please help.
Hi Sonia,
I hope you received my email.
Kind regards,
Jessah Shaw
Nutritionist