Research has found that some people with celiac disease have an autoimmune disease that destroys their bones!
Celiac disease (also known as gluten intolerance) is an autoimmune disease whereby the consumption of gluten causes damage to the lining of the digestive tract, and inflammation and damage to other organs and tissues in the body.
Gluten is found in wheat, rye, oats, barley, spelt and many processed foods. People with celiac disease need to strictly avoid these foods for life in order to maintain good health.
Celiac disease commonly produces symptoms such as abdominal bloating, diarrhea, constipation and fatigue. However, it also has the potential to cause serious health problems such as infertility, osteoporosis, lymphoma, type 1 diabetes and thyroid disease.
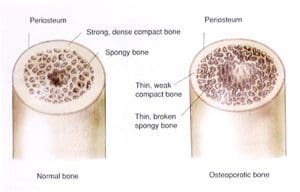
It has long been known that people with celiac disease are at increased risk of osteoporosis, and every patient diagnosed with osteoporosis should be tested for celiac disease.
This is because celiac disease disrupts the absorption of minerals in the digestive tract, and compromises liver function. Therefore people with the condition end up deficient in calcium and vitamin D.
This deficiency can be corrected once a person adopts a gluten free diet, but the problem is celiac disease often goes undiagnosed for decades. That is a very long time to be nutrient deficient and it certainly takes its toll on the bones.
So the good news is that adherence to a gluten free diet and the use of calcium and vitamin D supplements can go a long way towards improving the bone density of coeliacs. However not all celiacs get an improvement in their bone density; some progress to more severe osteoporosis which requires medication.
A possible explanation for this phenomenon is the discovery of osteoprotegerin auto-antibodies.
What this means is that some people with celiac disease develop osteoporosis because their immune system attacks and destroys their bones.
Autoimmune disease is frighteningly common; examples of some autoimmune diseases include Hashimoto’s thyroiditis (causing hypothyroidism), type 1 diabetes, rheumatoid arthritis, lupus and multiple sclerosis.
In all autoimmune diseases the immune system attacks and destroys the body’s tissues, as though they were a foreign invader.
Bone is largely made up of living cells, therefore new bone is continually being formed, while old bone gets broken down.
Researchers have only just discovered a protein called osteoprotegerin; it controls how much bone gets broken down. Researchers at The Institute of Genetics and Molecular Medicine at the University of Edinburgh found that 20 percent of celiacs produce antibodies that target this important bone protein.
Celiac disease affects approximately one in 100 Australians, therefore this new discovery could be a significant cause of osteoporosis in this country.
This discovery is still in the research stage, therefore testing for these antibodies is not yet available. However, it highlights the importance of addressing the immune system and reducing inflammation in all celiac patients.
People with celiac disease have an over stimulated immune system and they may produce several different types of antibodies against a number of organs and tissues. Avoiding gluten entirely is just the first step in improving immune system function.
There are a number of other effective strategies to reduce systemic inflammation and reduce the risk of autoimmune disease if you are a coeliac, these include:
- Avoid dairy products. The protein in milk (casein) is an immune system irritant for most celiacs. Lactose free milk is no better because lactose is a sugar and it is the protein in milk is the problem.
- Supplement with vitamin D and selenium. Vitamin D is formed in our body when sunlight hits our skin, however many people do not spend enough time outdoors in order to manufacture enough of it. Vitamin D deficiency can promote and aggravate all autoimmune disease. Selenium is a mineral that is very low in the soil in Australia and New Zealand, therefore it is almost impossible to obtain enough of it through diet alone. Selenium deficiency increases the risk of infections, allergies and autoimmune disease. A therapeutic daily dose of vitamin D is 1000 IU and 200 mcg of selenium.
- Take an omega 3 fish oil supplement. Fish oil is one of the strongest natural anti inflammatory agents there is. Even if you regularly eat fish, your immune system will greatly benefit from the omega 3 fats in fish oil. Liquid fish oil is usually more potent and better quality than fish oil capsules.
- Take a good quality probiotic. A probiotic is a good bacteria supplement, such as acidophilus and bifidus. Good bacteria in the bowel produce anti-inflammatory substances, whereas bad bacteria in the bowel produce highly inflammatory substances. The research done on probiotics indicates that effective doses can only be obtained through a supplement (capsules or powder), rather than foods such as yogurt.
- Stress less. Stress has a disastrous effect on the immune system and aggravates all autoimmune disease.
- Try to get enough good quality sleep. Sleep has a healing effect on your immune system and it reduces the production of inflammatory chemicals in your body.